- Name
- MDQSAT-1A
- Alternate Names
- "Juana Azurduy"
- Satellite ID
- LIMQ-1213-0513-2634-2255
- Temporary NORAD ID
- 99239
- Followed NORAD ID
- None
- Website
- https://www.innova-space.com/en/
- Country of Origin
-
Argentina
Satellite has re-entered
Satellite is reported to be transmitting at an uncoordinated or denied frequency. Details
- Launch Date
- 2023-01-02T14:55:00+00:00
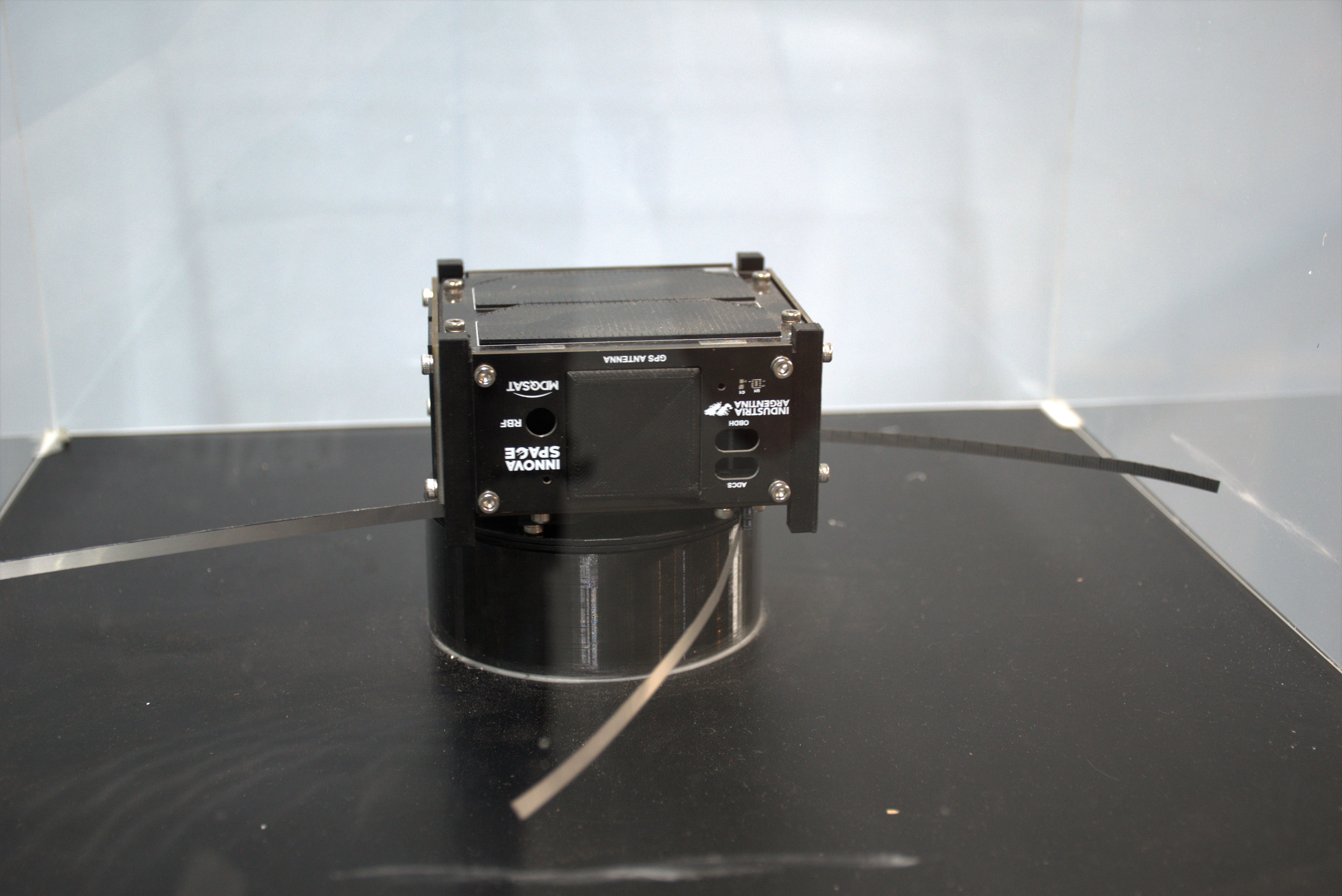
The MDQSAT-1A satellite, "Juana Azurduy", is the second in the "Libertadores de América" constellation. It’s a 0.5U CubeSat (10 x 10 x 5cm) and it weights 549g.
MDQSAT-1A/B are proof of concept for IoT communications through picosatellites in LEO. They have UHF communications (1W LoRa), stabilization through magnetorquers, a GNSS receiver, 3J solar cells and a Li-Ion battery. They also have temperature, current, light, and absolute orientation sensors that are needed for the satellite to operate and their data is sent as housekeeping telemetry.
They are developed by Innova Space in Argentina and their main purpose is to test the satellite platform for use in future missions.
- Type
- Transmitter
- Downlink Mode
- LoRa
- Downlink Frequency
- 437800000
- IARU Coordination
- IARU Uncoordinated
- Type
- Transmitter
- Downlink Mode
- LoRa
- Downlink Frequency
- 436900000
- IARU Coordination
- IARU Uncoordinated
No observations recorded for MDQSAT-1A in the last 24h